RPi Intelligent Security System
Project by Dongze Yue, Yixiao Zhang
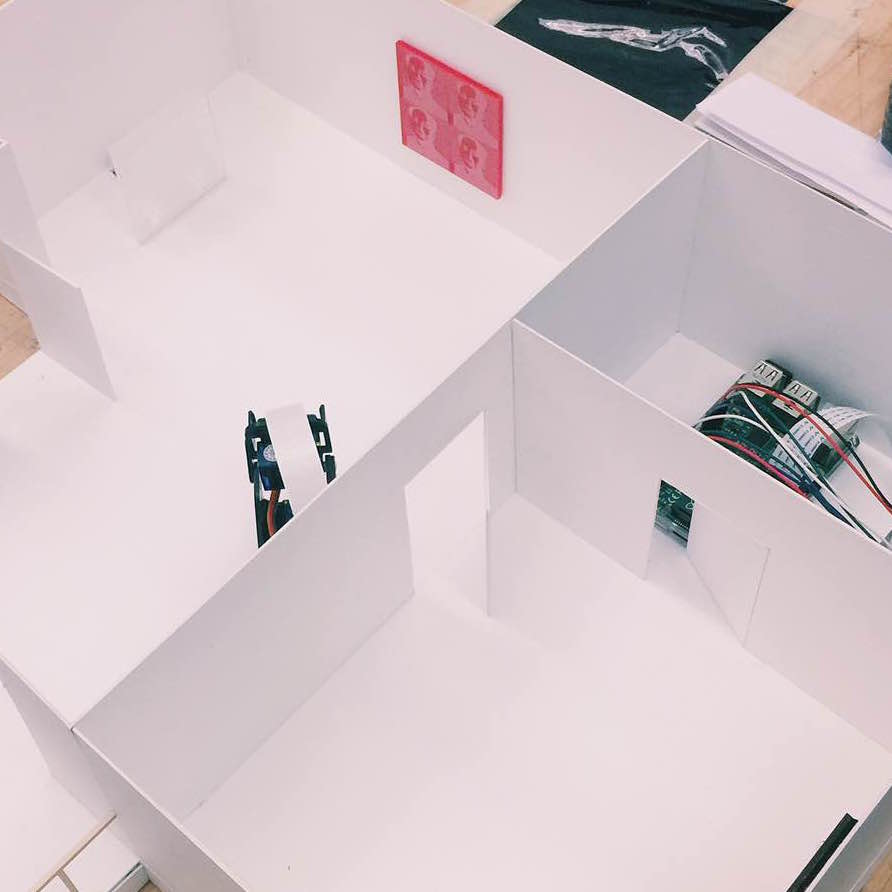

Project Overview
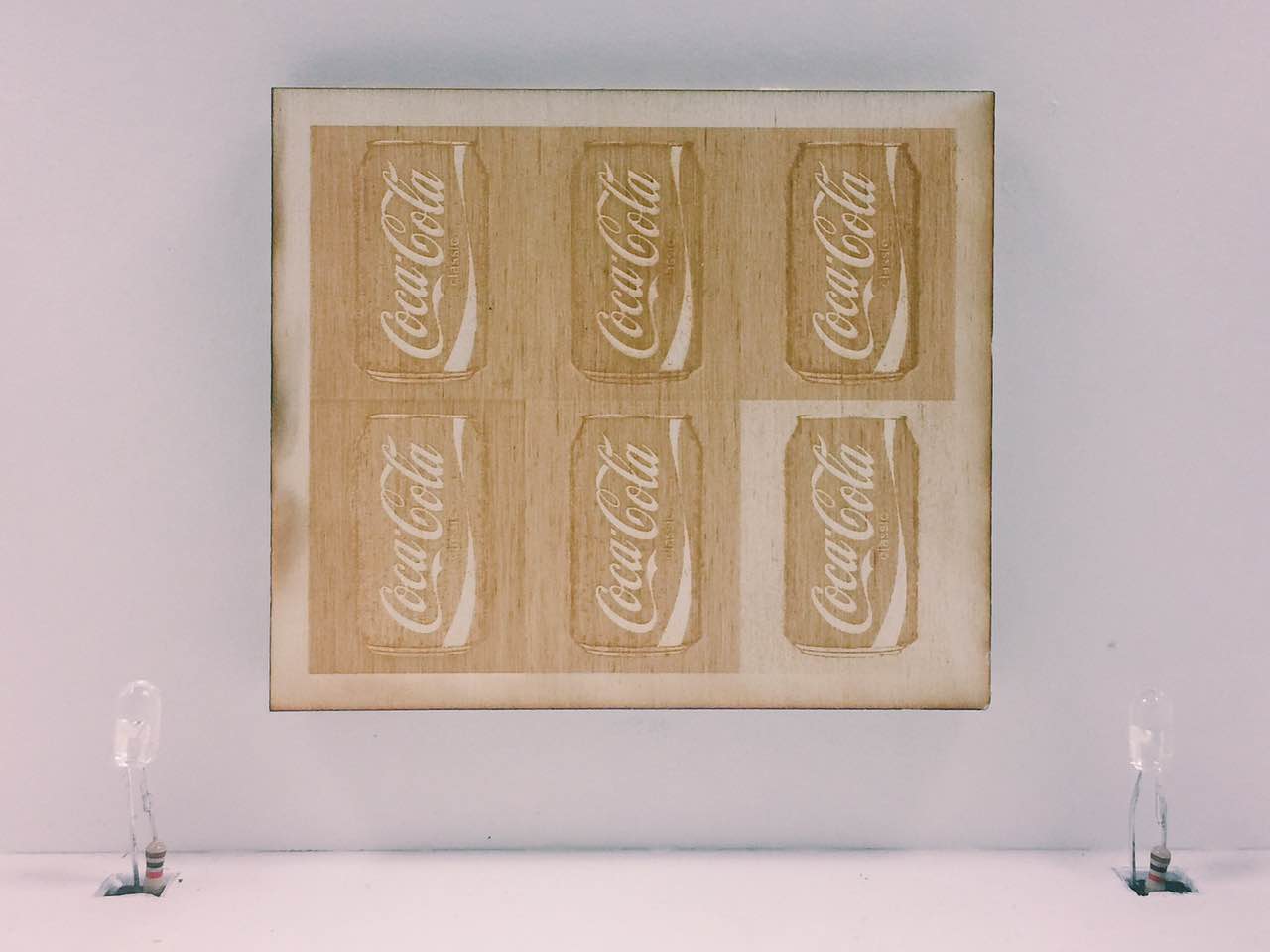

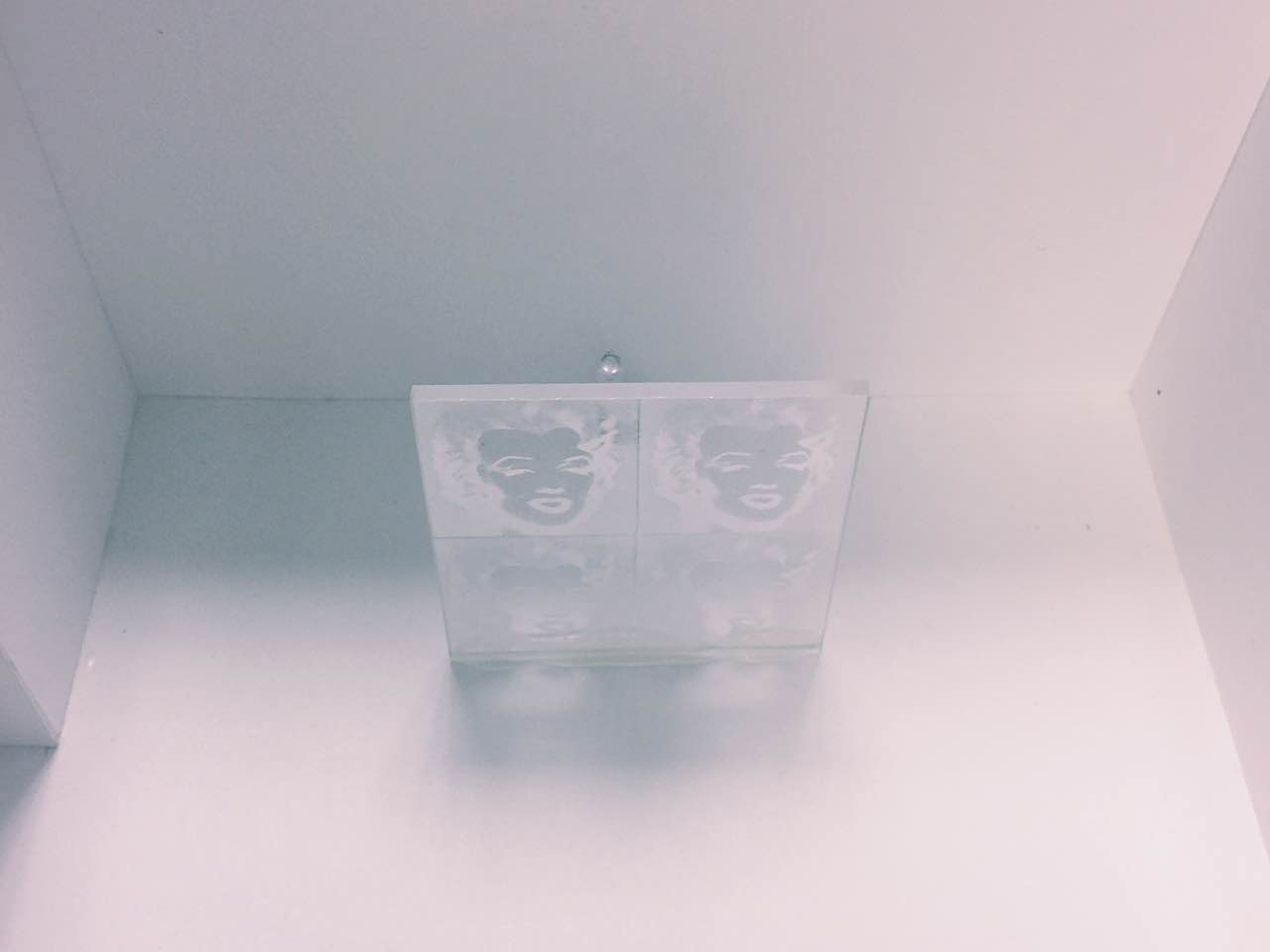
Gallery Artwork
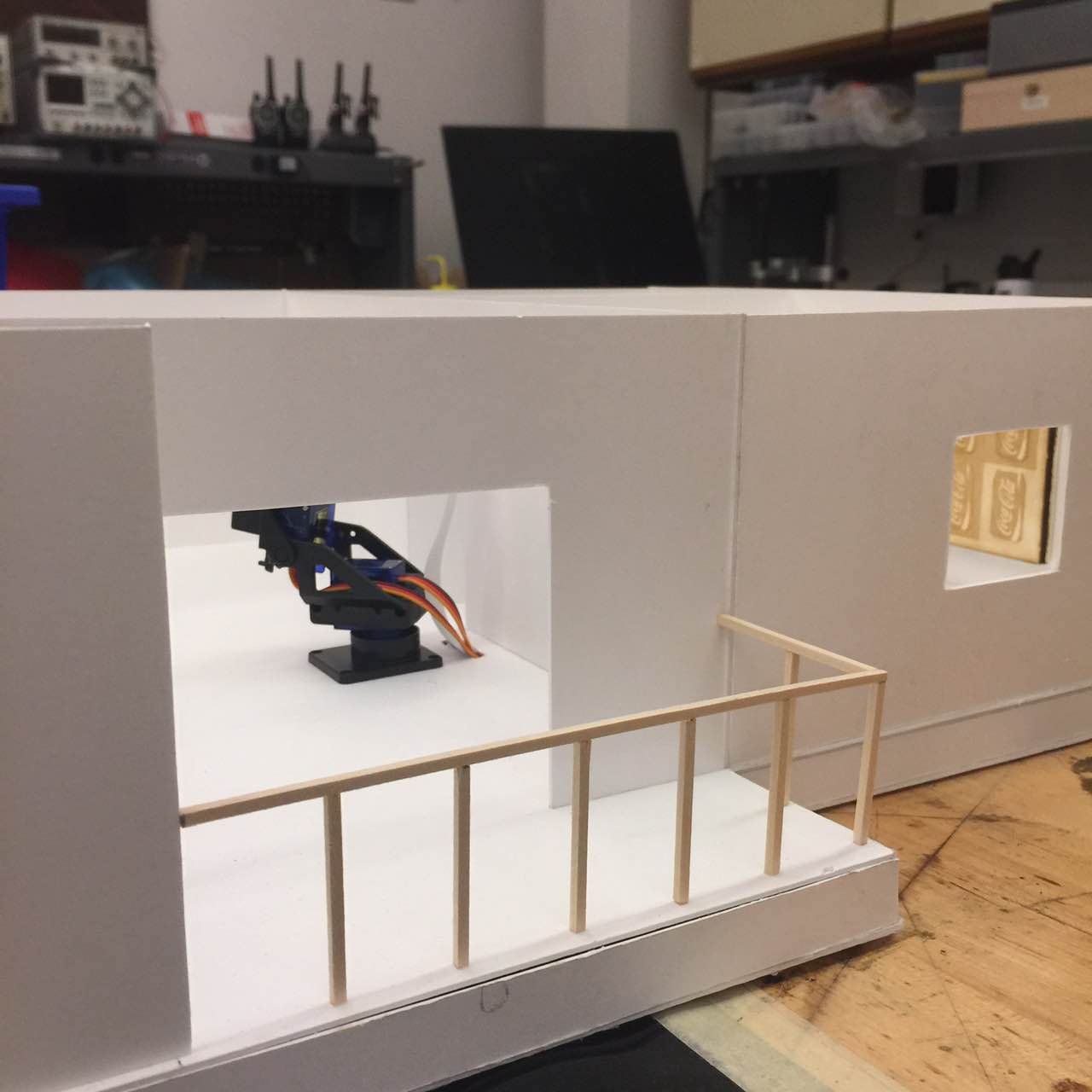

Security Camera
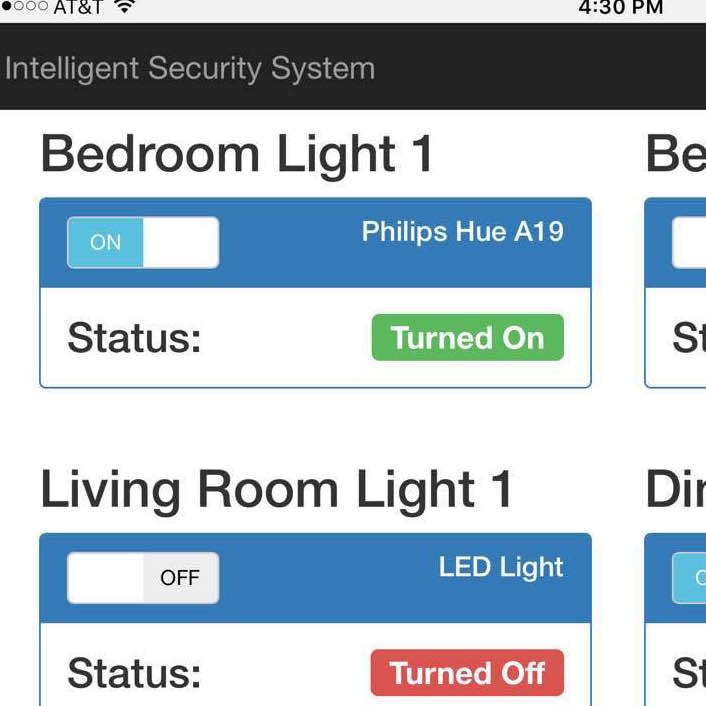
Front-end
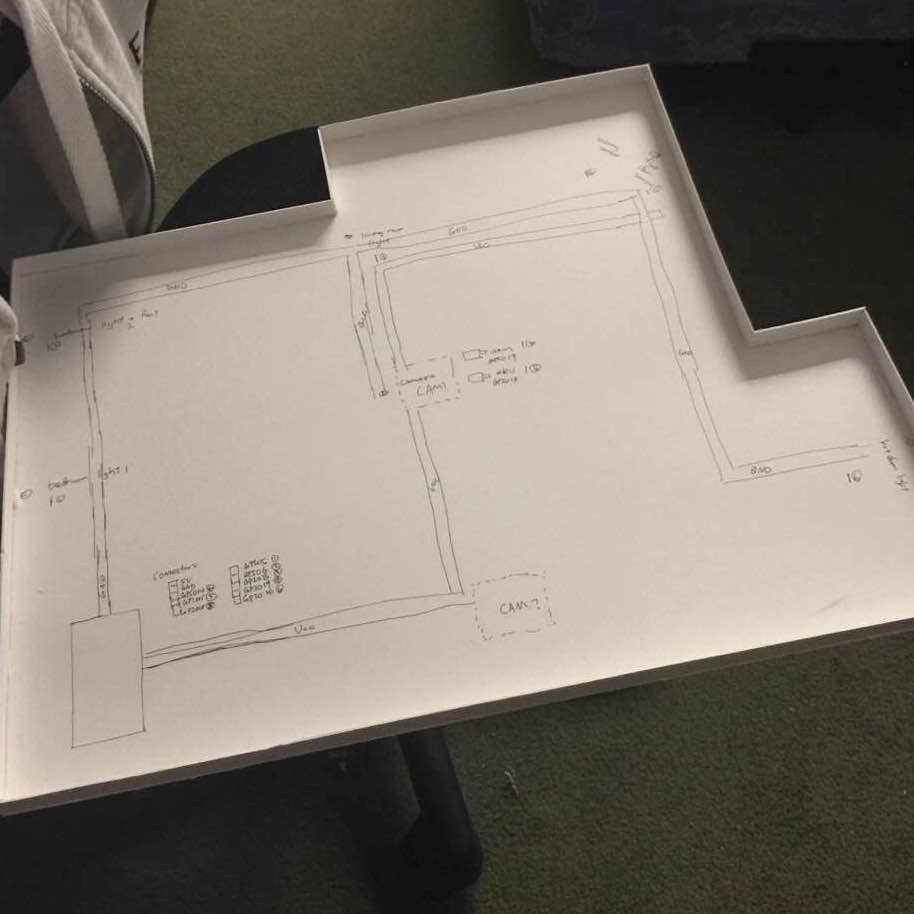
Base-plate
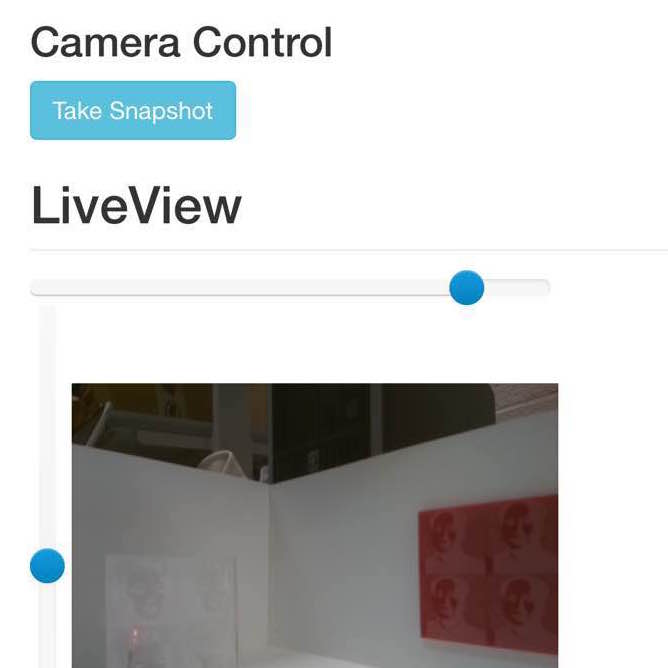
Interactiveness

Project Objective:
- Build an intelligent security system that can monitor a house and control all the household electrical appliances through a web interface.
- Event-driven intrusion detection and multi-level security settings.
- Modular design that is suitable for any additional peripheral hardware.
- Modules communicate via socket interface so that remote devices can also join the security network.
Demonstration Video
Introduction
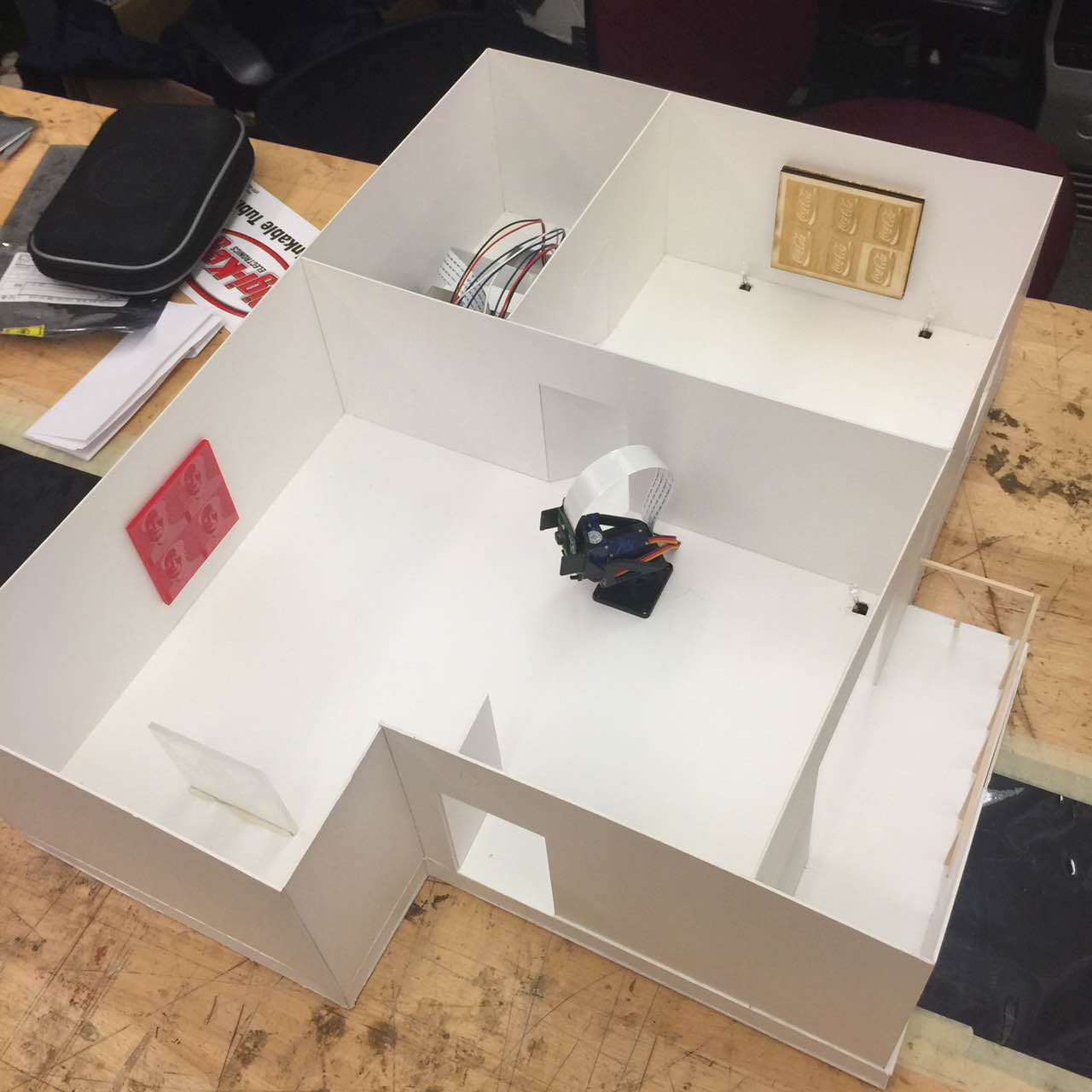
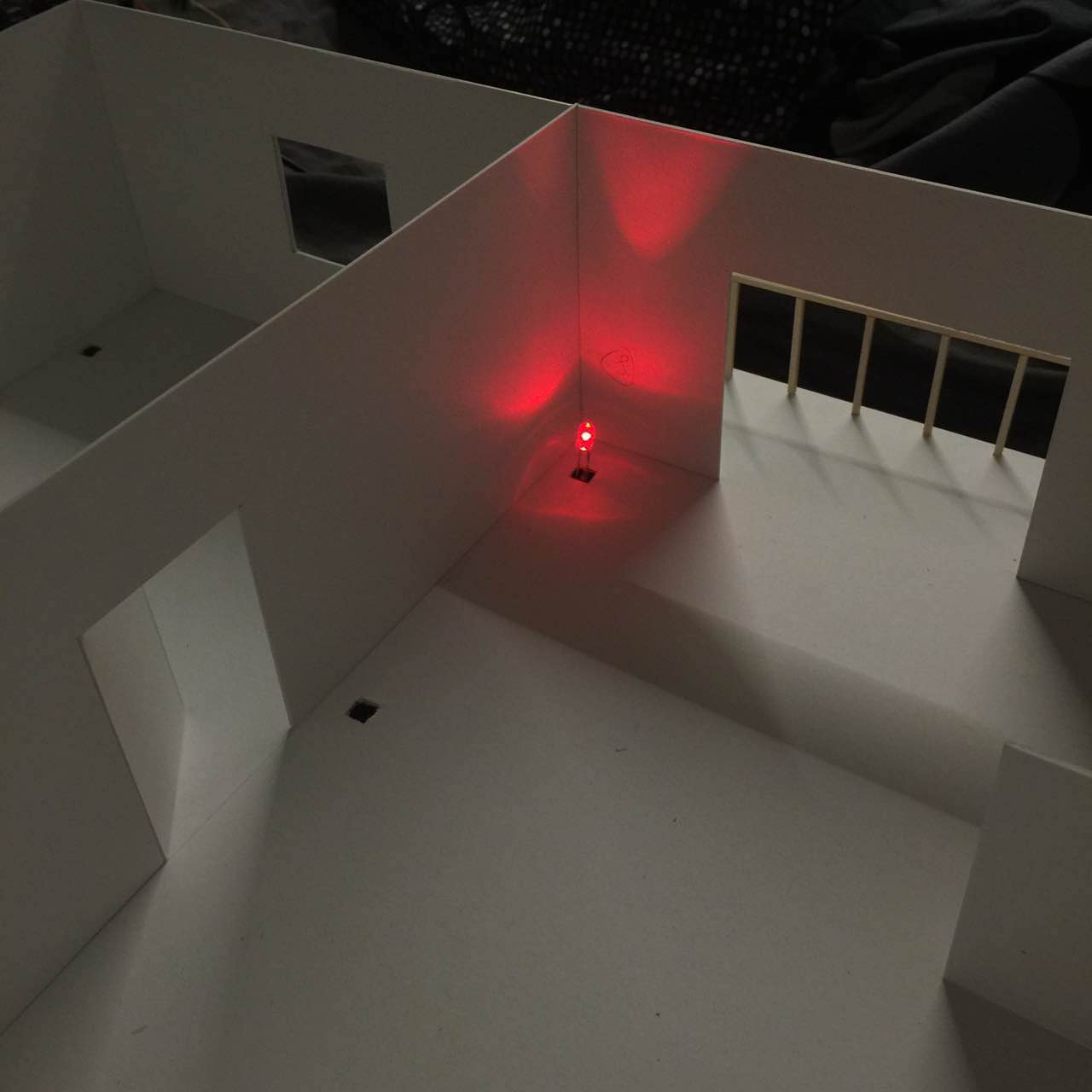
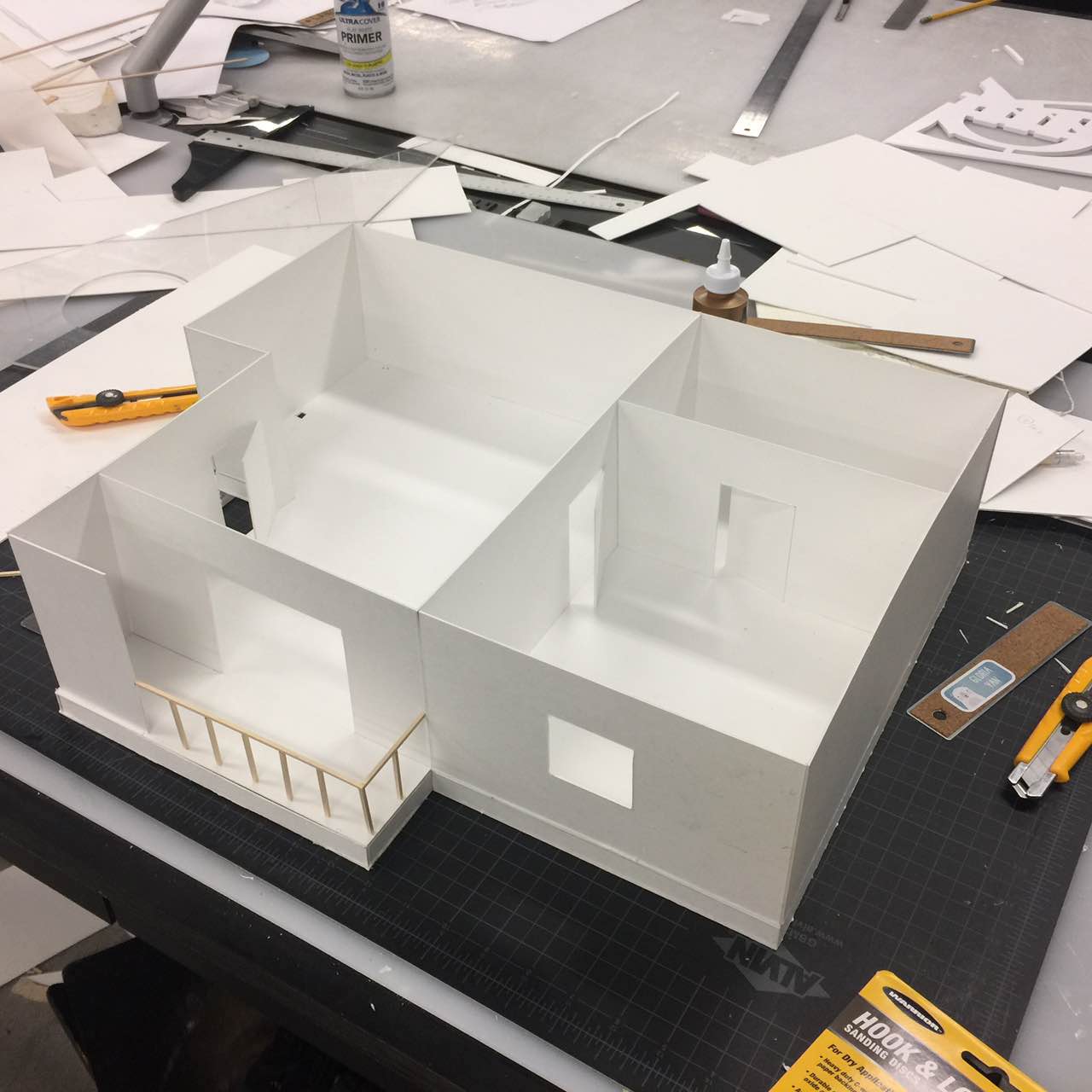
We built a smart home security system and server on Raspberry Pi that is capable of live-monitoring of the security footage, moving the surveillance camera’s viewing angle, detecting intrusion and controlling other parameters such as lighting and air conditioning in the house. By logging in to the web interface served by the Raspberry Pi, we can easily turn on/off a light at home and watch live feed from the camera. We can also change the azimuth and elevation angle of the camera’s base mount so we can look at any wanted angle. We also fitted our design into a miniature interior design model so that we can fully demonstrate the robustness and functionalities of our design within the model.

Hardware Design
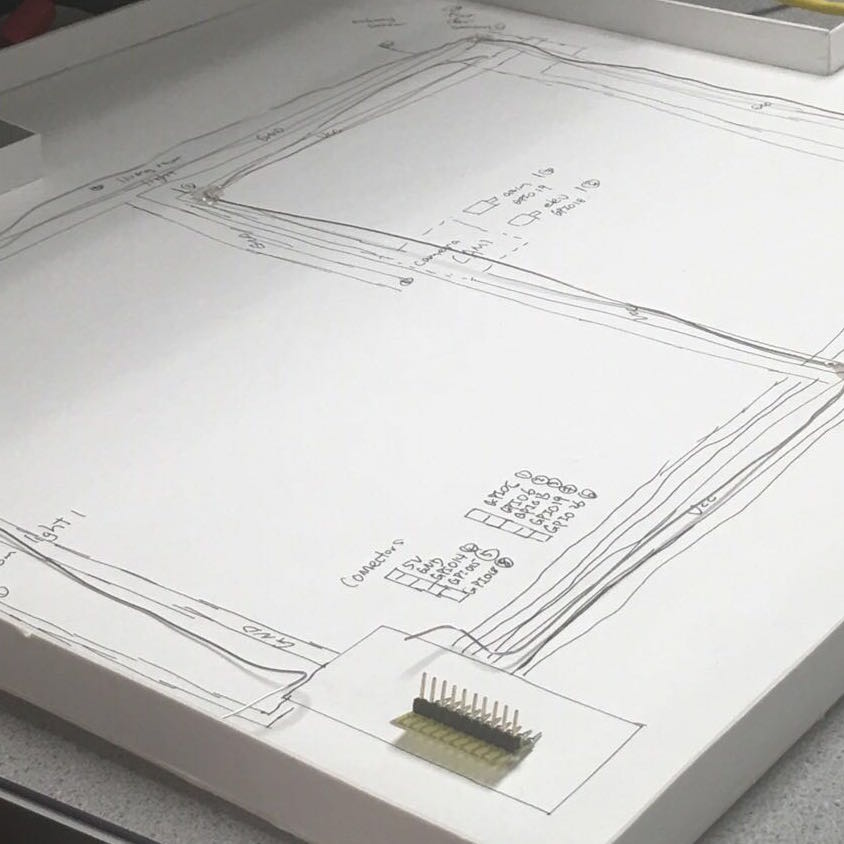
Circuit Design
In order to fit our design in the interior design model, we created another basement layer beneath the house and wired all the circuitry on the base-plate. We also want to ensure that connection from the base-plate to the Raspberry Pi is manageable and tidy, therefore we drew a wiring sketch on the plate and attached wires onto the sketch. We also soldered a 10-pin connector at the edge of the base-plate so that the Raspberry Pi can directly be wired onto the connector. The wiring plan is attached below for clarity.
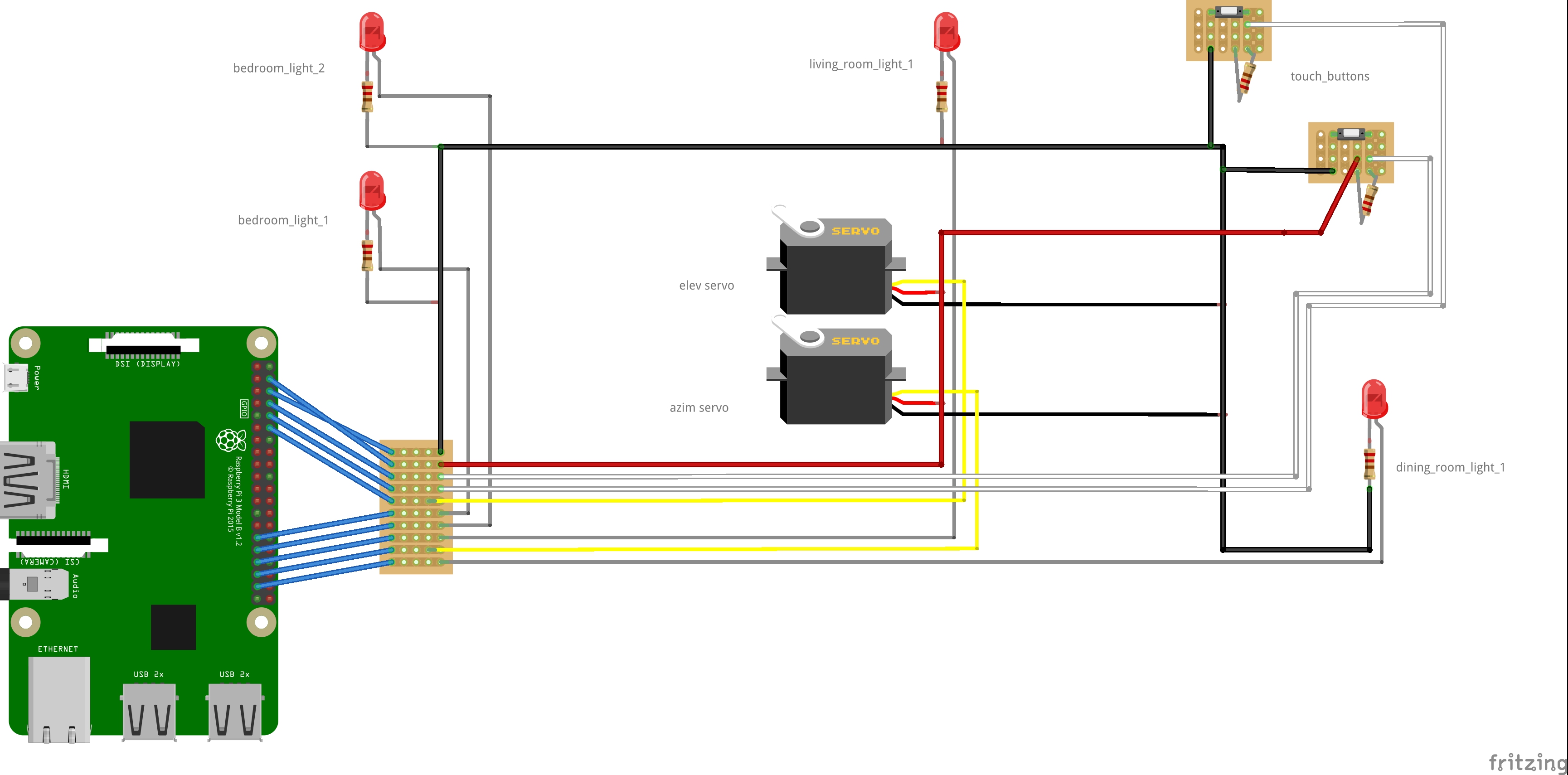
Circuit schematics of base-plate design
Raspberry Pi
The Raspberry Pi controls all the signals that is being wired to the house, including two separate PWM waves. However, when we tried to use the RPi.GPIO library to output PWM to an output pin, we notice a significant wiggle and shiver on the PWM pulses as we increase the amount of processes running in the background. This is exactly due to that software-controlled PWM waves will become unstable as the operating system is not real-time and try to schedule other tasks at the same time when there should be a change on the pin. We investigated into this issue and looked up for resources so that might solve the problem. We ended up finding out that the Raspberry Pi actually supported hardware PWM and there is a library named “pigpio” to enable it, although the hardware PWM is only configurable on a limit number of pins.
After we setup the hardware PWM on the Raspberry Pi, we tested the pulse wave with an oscilloscope and ensured that the pulse is very stable when other python processes are running. Then we picked GPIO 18 and GPIO 19 as output of two hardware PWM waves. In order to make connection more tidy, we picked the 10 consecutive pins near GPIO 18 and 19 and programmed them to be input/output correspondingly, as the schematics diagram above demonstrates.

Servo, LEDs and button control
The servos used in the system are TowerPro micro stepper servos that takes in three inputs: Vcc, Ground and Signal. The signal pin takes in a pulse-width-modulated (PWM) wave as reference of where the servo should be rotating to. By adjusting the duty cycle of the PWM wave, we are able to control the servo to point at any angle within the rotation range specified by the servo.
In order to simulate smart home lighting system, we turn on and off LEDs using a toggleLED() function written in the lighting control script. However, in real life situation, we would configure that specific function into a command that drives the actual lighting device. Or the Raspberry Pi’s output can be relayed to toggle a larger home appliance circuit.
Software Design
Web Framework
The web framework is developed using Python’s microframework library, flask. There will be an instance of flask app running in the background and serve a web page on http://ip-address-of-pi:5000/. The framework handles http get and post requests as python functions. Therefore, whenever user triggers a input on the front-end, the information will be encoded as post request going to the server. The server then decodes the request and issues the messaging interface to control/update designated parameters.
The web page is developed using Bootstrap, a fast-deploy front-end web framework. Using the template files available, we were able to build our website with pleasing format and elegant layout.
Messaging Interface
The messaging interface utilizes python socket interface to realize cross communication between applications, with a complete set of application-layer network protocol designed and implemented specifically for this project. The center of the messaging interface is a MessageServer, which accepts from other applications, and forwards data packets between them. All other applications instantiate a Client module and establishes point-to-point connections with the MessageServer.
Update
“Update” is a special message we designed for each member to update the status of themselves or the system with each other. It includes several components:
- Source: sender of the update, either a client type name or ‘msg_server’ Destination: receiver list of the update. Any Client receiving an update not for itself will automatically drop the message; MessageServer forwards an update to all clients in the destination list. In current build, the destination list is always all members in the network.
- Name: unique identification of each updates flooding around in the messaging system. e.g. “servo_azim”, “bedroom_light_1”.
- Version: A counter increased by 1 every time a new update of the same name is constructed. When every node, MessageServer or a Client, receives a new version of update, it stores these information locally, replacing the old version if there is any.
- Payload: content of the update. This can be commands like turning a light on/off.
System Mechanics
A loop running in MessageServer polls on each of its socket every cycle. It looks for new connections from the listening port, and incoming data packets from other Client sockets. It forwards packets to all Clients in the destination list. They wa Clients receive messages from socket is on application discretion: the LED/servo controllers need to constantly poll on their sockets to keep up with latest commands, while WebServer can just sleep and do not update anything until there is user operations. When Clients need to communicate with each other, all messages are sent through the MessageServer. The “Update” messaging scheme ensures that all members always take the latest version of a message, so the whole system is synchronized.
Fault Handling
When one program runs into an error, it is important to ensure that functionality of rest of the system is not affected. When MessageServer detects a disconnection on any node, it closes the socket bound to this connection and kicks it out from the running node list. Then it broadcasts an updated list of network members, so that other nodes will stop sending messages to the disconnected node. The error program can be rerun and join the system again by connecting to the listening port. The MessageServer would then resend the node all its latest version updates and broadcast the new running list, so that the status before disconnecting can be resumed.
Messaging Format
Because data packets are concatenated one after another in the input buffer of a socket, universal rules under which nodes can talk to each other need to be pre-defined to ensure correct message handling. In our interface, each message is started with an uppercase letter like “I”(“Init”), “T” (“Type”), from which type of a message is identified. An “\n” character is automatically concatenated to every outgoing message so that messages can be separated from each other simply by string stripping. Besides, each message is constructed from multiple components, a “/” character is used to separate fields.
Type
A messaging system is started when MessageServer program starts running on background of the Raspberry-Pi. It opens up a non-blocking socket listening for incoming connections. When a new connection comes in, a new socket bound to this particular connection is created. Then, MessageServer sends out a “Type” request for identification of remote node. When a reply matches with a type in the local Client list, a (type, socket) pair is stored in a list; otherwise the connection is dropped.
Init
After all clients have connected and been identified, the MessageServer sends out an “Init” request, informing all Clients to initiate their own systems. Clients then sends feedback confirming their initiation. The MessageServer then broadcast a complete list of Client nodes in this network.
System Termination
A Client node can be closed in two ways: first, receiving a “close request” broadcasted from WebServer upon user operation; second, detecting a socket lost connection on MessageServer side. A MessageServer would continue running unless receiving a “close request”.

Gallery Artwork, Coca Cola by Andy Warhol, laser engraved
Running Nodes in Current Build
In the current build, there are totally 5 nodes and 1 message server running in the background. This combination is able to achieve LED, servo controlling, multi-level security logic, front-end message update and request, and touch button detection. All the nodes will be introduced below.
Messaging Server
Master messaging host that starts up at the given host and port name. It waits for successful connections with all the nodes and assign each node with a separate designated connection object. It keeps the connection objects in a dictionary so that every time the server wants to route the message to a designated target, it can perform a lookup in the dictionary.
LED Controller
Controls the LED by setting up the GPIO port and writes HIGH and LOW to it according to the control message received. Also sends back a confirmation message to signal the completion of this control message.
Servo Controller
Initializes hardware PWM on two GPIO pins to drive both the azimuth and elevation servo. It converts the target angle from the control message to the notion of duty cycle and sets the corresponding data.
Button Detector
Initializes a GPIO input callback function that will trigger an event detection message and broadcast the message to the network.
Security System
Contains an internal state variable that stores the current security state. When events are triggered, the node will react and send control messages to corresponding nodes based on the security state. The security state is directly modifiable by a state modify message that can be sent from the front-end.
Web Server
Instead of a stand-alone python process, the web server node is a library attached to the flask application. The application asynchronously constructs control requests and send them down the network. There is also a blocking polling function that waits for a certain confirmation message to travel back from the network.
Project Result
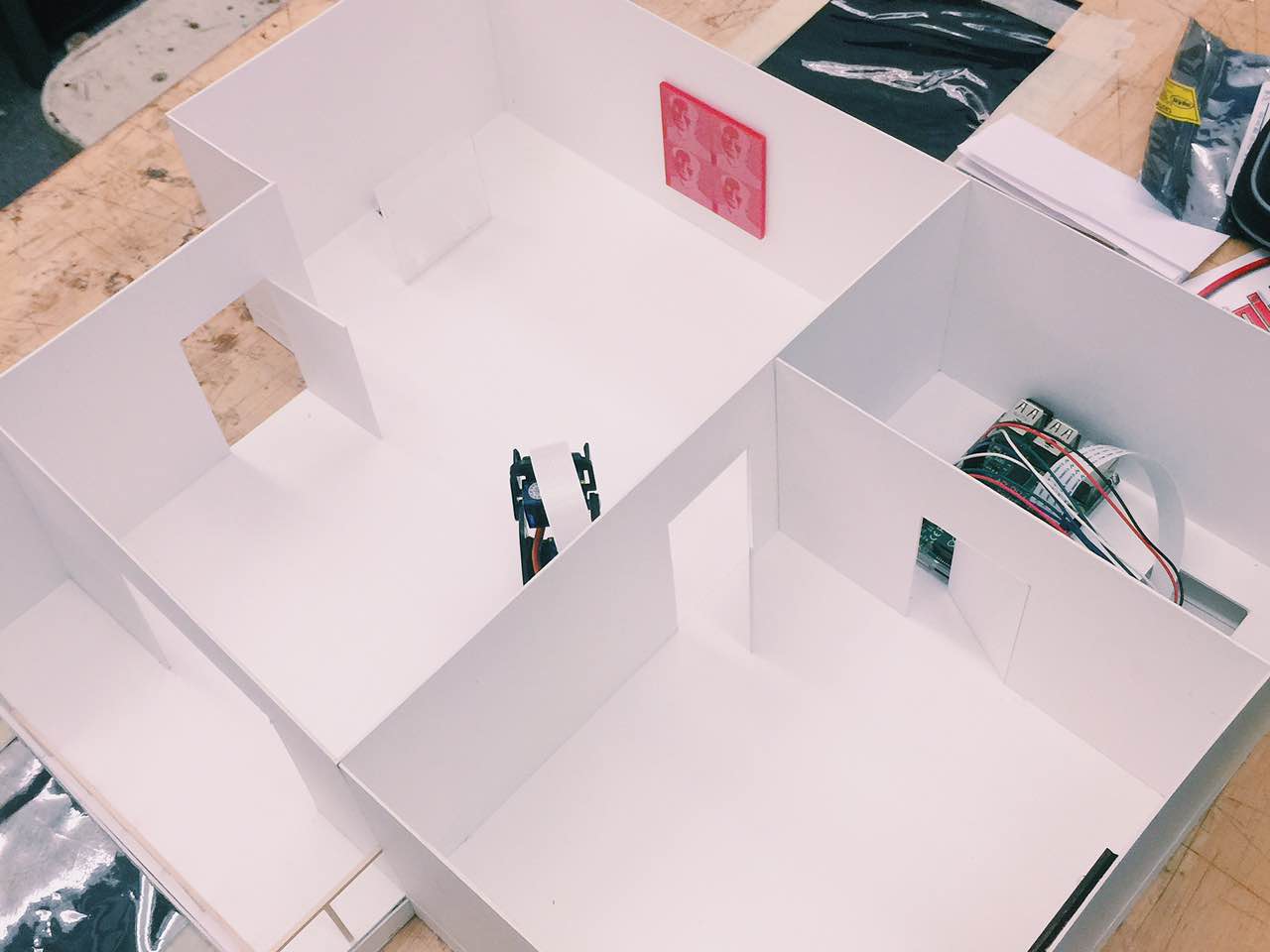

Security System in an Interior Design Model
As the result of our design, we have a fully working web page can set the current security mode of the system. There are totally four modes available:
- Easy Secure: Any events triggered at the front door or balcony will result in a camera movement to point at the event location. A snapshot will be taken at the location and it will be logged as event detected in the log file.
- Demo Mode: A demonstration mode that shows the basic circuitry beneath the system. It lights up the LEDs in sequential order and the servo will rotate from left to the right in a pattern.
- Highly Secure: Verbose logging mode, basically Easy Secure mode plus a lot more logging of all the events.
- Manual: Manual takeover of the system. Disable all the automated functionalities.
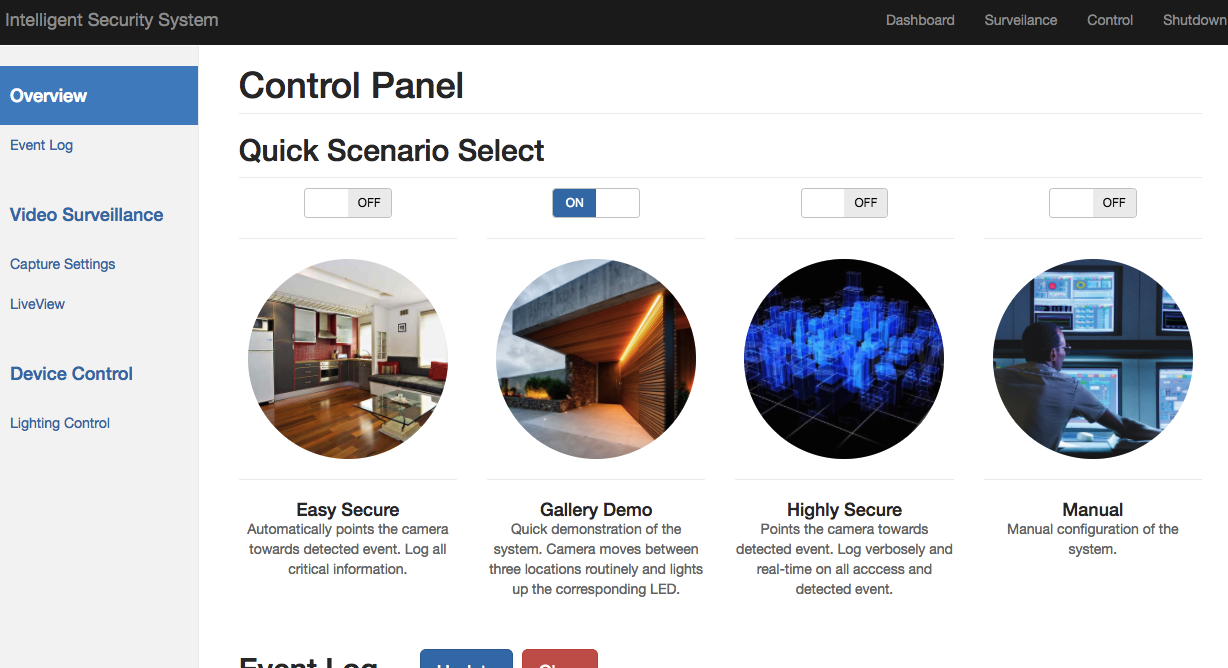
Interactive Front-end
And by toggling between the four modes, the web server receives the current mode and broadcasts the mode switching message to the network. The messaging network receives the message and re-broadcast the message again to all the existing nodes. The security system node receives this mode change and updates its internal security level. Therefore, the security system mode can constantly issue command to the other nodes according to the security level. For example, if the security level is Easy Secure, when the push button pressed, an intrusion will be detected by the touch button node, and the touch button node will send a message of detected event to the network. Other nodes that doesn’t understand the message will drop it, and the security center will see the message and decode it. It will then send servo movement messages to the servo control node and drive the servos to point the camera at the location and calls the camera subprocess to take a snapshot. When the front-end sets the security level to manual, the security system node will no longer trigger servo movement when reading an event detection message.
Future Work
By using this robust modular design, we can expand the network if hardware permits as much as possible. There can be more systems connected to the messaging network to be controlled. There can be a dedicated data logger node that will record all the messages on the run. There can also be a separate temperature control node that reads sensor readings and send out commands to control a AC in the network.
Here are several issues we need to resolve with going large scale.
- efficiency: If we have hundreds of nodes in the network and we want to send a designated message to only one node, there is no point of broadcasting all packets to all the nodes. We will look into the solution for faster sending and better message formats.
- Latency and congestion: The Message Server is essentially a data bus that all messages need to go through. because all hardware controller as well as the Message Server need to loop on socket polling, when load of RPi gets too high, messages can be queued up in the output buffer of sockets and not getting a chance to be sent forever. Here are several aspect to look at to resolve the problem:
- carefully schedule all processes to ensure that all sockets have a chance to send
- Add an additional output buffer to hold outputting data, and make data in one socket only go out once in every socket
- Because our interface is completely compatible with applications on multiple machines, we can distribute traffic flow by adding in another RPi that run another Message Server, and connecting the two Message Servers together as routers in the network.
Work Distribution
Project group picture

Steven (Dongze) Yue
dy85@cornell.edu
Designed the front-end web interface as well as the base-plate for the interior design model. Installed all the electrical components into the house. Also wrote the interactive flask application that handles post requests and convert them into control messages that can be sent down the network.

Yixiao Zhang
yz624@cornell.edu
Designed and constructed the back-end messaging interface and conducted initial software-hardware testing.
Acknowledgement
The interior design model used in the project was manually created from a 2D stock footage found online. The dimensions of the walls are then measured to be built in 3D. This project cannot be done without tremendous help from a friend of ours, Gloria Yan, a student at Cornell Architecture, Art and Planning School. Professor Skovira also helped us with refining the ideas of our design as well as finalizing it into a exhibition-ready product.

Parts List
- Raspberry Pi $35.00
- Raspberry Pi Camera V2 $25.00
- Mini Pan-Tilt Kit - Assembled with Micro Servos - $18.95
- LEDs, Resistors and Wires - Provided in lab
- Chipboards(for model) - $5.00
Total: $83.95
References
PiCamera DocumentFlask Installation
MJPG-Streamer
Tower Pro Servo Datasheet
Bootstrap
Pigpio Library
R-Pi GPIO Document
Python Socket
Code Appendix
message.py
Main messaging server
import socket
from client import *
from time import sleep
import select
import sys
import errno
class Terminal:
uid = 0
node = None
addr = None
terminal_type = ''
input_buffer = ''
output_buffer = ''
def __init__(self, terminal_type = 'unknown'):
pass
class MessageServer(Message):
terminals = {}
running = {}
unknown = []
buf = {}
connected = False
run = False
try_initiate = False
messenger_type = 'msg_server'
closed = False
def __init__(self, *args):
for arg in args:
if type(arg) is str:
self.terminals[arg] = None
self.running[arg] = None
self.buf[arg] = None
# ========== message handler end =================
def _set_client(self, client, name):
found = False
for key in self.terminals.keys():
key_word = "/{}/".format(key.strip())
debug_print("MessageServer set client: ", key_word)
debug_print("MessageServer set client: name: ", name)
if name.find(key_word)!=-1:
self.terminals[key] = client
self.unknown.remove(client)
debug_print('MessageServer set client: connected to', key)
found = True
if not found:
debug_print("MessageServer set client: Unresolved cleint name!")
return
connect_flag = True
for v in self.terminals.values():
if v is None:
connect_flag = False
self.connected = connect_flag
# try to initiate system if system not running and try initiate flag set true
if (self.connected and not self.run and self.try_initiate):
self.send_to_all('I')
debug_print('MessageServer set client: init system')
def _try_run(self, client, name):
found = False
for key in self.terminals.keys():
key_word = "/{}/".format(key.strip())
debug_print(key_word)
debug_print("MessageServer try run ","name: ", name)
if name.find(key_word)!=-1:
self.running[key] = client
debug_print("MessageServer try run ",'client', key, 'sends initialization feedback')
found = True
break
if not found:
debug_print("MessageServer try run ","Unresolved cleint name!")
return
running_flag = True
for v in self.running.values():
if v == None:
running_flag = False
self.run = running_flag
if self.run:
self.try_initiate == False
def _resolve_msg(self, client, msg):
#print "resolving message... " + msg
if msg == '':
return
Message._resolve_msg(self,client, msg)
if msg[0] == 'T':
debug_print("MessageServer resolve msg ",'received type from client')
self._set_client(client, msg[1:])
if msg[0] == 'I':
debug_print("MessageServer resolve msg ",'received initiate response from client')
self._try_run(client, msg[1:])
if msg[0] == 'U':
debug_print ("MessageServer resolve msg ",'update')
name = self.update_msg(msg[1:])
#debug_print(name)
if name in self.update_msg_list.keys():
self.forward(self.update_msg_list[name].dest, msg)
if msg[0] == 'X':
for v in self.terminals:
print v
if (msg[2:] != v):
self.terminals[v].send('X\n')
self.terminals[v].shutdown(socket.SHUT_RDWR)
self.close()
def close(self):
self.sock.close()
self.closed = True
# ========== message handler end =================
def send_to_all(self, s):
if not type(s) is str:
return
for v in self.get_terminal_list():
v.send(s+'\n')
def try_accept(self):
c, addr = self.sock.accept()
debug_print("MessageServer try accept: ",'Got connection from ', addr)
c.setblocking(0)
self.unknown.append(c)
c.send('T\n')
debug_print("MessageServer try accept: ", "sending'T'")
def init_connections(self, port):
# Init socket
self.sock = socket.socket()
self.host = socket.gethostname()
self.port = port
debug_print("MessageServer init connections: ", 'host name: ' + self.host)
self.sock.setsockopt(socket.SOL_SOCKET, socket.SO_REUSEADDR, 1)
self.sock.bind((self.host, self.port))
# set the socket nonblocking
self.sock.setblocking(0)
# Listen on the socket
self.sock.listen(3)
self.try_initiate = True
def send(self, name, msg):
self.terminals[name].send(msg+'\n')
def get_terminal_list(self):
return [v for v in msg.terminals.values() if not v is None]
def get_type_list(self):
return [k for k, v in msg.terminals.iteritems() if not v is None]
def set_nonblocking_all(self):
for v in self.terminals.values():
v.setblocking(0)
def forward(self, dest_list, msg):
for d in dest_list:
if d != self.messenger_type:
self.send(d, msg)
def update_network(self):
l = self.get_type_list()
if len(l) == 0:
return
p = ';'.join(l)
s = self.construct_update(l, 'network', p)
for n in l:
self.send(n, s)
msg = MessageServer('led_ctrl', 'servo_ctrl', 'button_ctrl', 'server', 'security_center')
msg.init_connections(12345)
while(not msg.closed):
sleep(0.1)
terminal_list = msg.get_terminal_list()
terminal_list.append(msg.sock)
terminal_list.extend(msg.unknown)
readable, writable, exceptional = select.select(terminal_list, [], [], 0)
for s in readable:
# accept connection from serving socket
if s is msg.sock:
msg.try_accept()
# read data from other socket readable
else:
msg.recv(s)
if not msg.run:
msg.update_network()
servo_controller.py
controls the two servos
import socket
from client import *
from time import sleep
import pigpio
class Servo():
runnint = False
current_angle = 0
def __init__(self, pi, pin, freq = 200, dc_min = 110000, dc_max = 390000, dc_start = 250000):
self.p = pi
self.pin = pin
self.freq = freq
self.dc_min = dc_min
self.dc_max = dc_max
self.dc = dc_start
self.current_angle = 50
self.p.hardware_PWM(self.pin, self.freq, self.dc)
def servo_set_angle(self,angle):
# restrict angle to max/min value
if angle > 100:
angle = 100
if angle < 0:
angle = 0
# save angle
self.current_angle = angle
# calculate dc
dc = self.dc_min+(self.dc_max-self.dc_min)*angle/100
self.dc = dc
self.p.hardware_PWM(self.pin, self.freq, self.dc)
debug_print('servo set angle: ', angle, dc)
def servo_start(self):
print "servo started"
def servo_stop(self):
self.p.write(self.pin, 0)
class Signal():
connected = False
initiated = False
class ServoCtrl(Client):
servo_control_list = {'servo_azim' : None, 'servo_elev' : None}
#mode = 0 #mode# 0: irresponsive to button 1: respond to button presses (at location) 2: periodical checking
waypoints = {'front_door': [50, 50], 'balcony': [92, 54], 'gallery' : [20, 47]}
def __init__(self, messenger_type, azim_pin=19, elev_pin=18, freq = 200, dc_min = 110000, dc_max = 390000, dc_start = 250000):
Client.__init__(self, messenger_type)
self.p = pigpio.pi()
self.servo_control_list['servo_azim'] = Servo(self.p, azim_pin, freq, dc_min, dc_max, dc_start)
self.servo_control_list['servo_elev'] = Servo(self.p, elev_pin, freq, dc_min, dc_max, dc_start)
self.mode = 0
def close(self):
self.server.close()
self.closed = True
for i in self.servo_control_list:
self.servo_control_list[i].servo_stop()
def resolve_msg(self, msg):
Client.resolve_msg(self, msg)
def send_status_update(self, name, payload):
if len(self.network) != 0:
s = self.construct_update(self.network, name+'_status', str(payload))
self.send(s)
def send_status_update(self, name, payload):
if len(self.network) != 0:
s = self.construct_update(self.network, name+'_status', str(payload))
self.send(s)
def set_position(self, azim, elev):
self.servo_control_list['servo_azim'].servo_set_angle(azim)
self.servo_control_list['servo_elev'].servo_set_angle(elev)
def _resolve_update_msg(self, name, payload):
# control servo
if name in self.servo_control_list.keys() and payload.isdigit():
payload = int(payload)
self.servo_control_list[name].servo_set_angle(payload)
self.send_status_update(name, str(self.servo_control_list[name].current_angle))
elif (name == "target_front_door"):
self.set_position(self.waypoints['front_door'][0],self.waypoints['front_door'][1])
elif (name == "target_balcony"):
self.set_position(self.waypoints['balcony'][0],self.waypoints['balcony'][1])
elif (name == "target_gallery"):
self.set_position(self.waypoints['gallery'][0],self.waypoints['gallery'][1])
elif (name == "servo_setmode"):
self.mode = int(payload)
else:
debug_print('unknown payload, ignoring ...')
return
self.send_status_update(name, payload)
port = 12345
host = socket.gethostname()
ctrl = ServoCtrl('servo_ctrl', 18, 19)
ctrl.init_connections(port, host)
angle = 0
direction = 0
count = 0
while(not ctrl.closed):
sleep(0.2)
ctrl.poll_msg([ctrl.server],[],[])
debug_print ("servo_ctrl: ", 'ctrl.initiated: ', ctrl.initiated)
ctrl.update_network()
if ctrl.mode == 1:
if direction == 0:
angle += 1
else:
angle -= 1
if angle>=100:
angle = 100
direction = 1
if angle <= 0:
angle = 0
direction = 0
ctrl.servo_control_list['servo_azim'].servo_set_angle(angle)
led_controller.py
controls the lighting in the house
import socket
from client import *
from time import sleep
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
class Signal():
connected = False
initiated = False
class LightingCtrl(Client):
lighting_control_list = {}
pin_list = {}
def __init__(self, type, pin_list):
Client.__init__(self, type)
for key, value in pin_list.iteritems():
self.lighting_control_list[key] = 0
self.pin_list[key] = int(pin_list[key])
GPIO.setup(self.pin_list[key], GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.output(self.pin_list[key], 0)
def resolve_msg(self, msg):
Client.resolve_msg(self, msg)
def send_status_update(self, name, payload):
if len(self.network) != 0:
s = self.construct_update(self.network, name+'_status', str(payload))
self.send(s)
def _resolve_update_msg(self, name, payload):
debug_print("resolve update msg: ", name, payload)
if "get_" in name:
if name[4:] in self.lighting_control_list.keys():
self.send_status_update(name[4:], self.lighting_control_list[name[4:]])
if name in self.lighting_control_list.keys():
self.set_light(name, payload)
def set_light(self, name, payload):
self.lighting_control_list[name] = 1 if payload == "true" else 0
self.ctrl_led()
self.send_status_update(name, payload)
def ctrl_led(self):
for key, value in self.lighting_control_list.iteritems():
GPIO.output(self.pin_list[key], int(value))
def close(self):
Client.close(self)
GPIO.cleanup()
port = 12345
host = socket.gethostname()
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
#lighting_control_list = {'bedroom_light_1' : 5, 'bedroom_light_2' : 6, 'dining_room_light_1' : 13}
lighting_control_list = {'bedroom_light_1': 5,'bedroom_light_2': 6, 'living_room_light_1' : 13, 'dining_room_light_1' : 26}
ctrl = LightingCtrl('led_ctrl', lighting_control_list)
ctrl.init_connections(port, host)
count = 0
while(not ctrl.closed):
sleep(0.2)
ctrl.poll_msg([ctrl.server],[],[])
ctrl.update_network()
#if ctrl.initiated:
#ctrl.set_led()
#ctrl.send_update_led()
buttons.py
detects button presses in the system
import socket
from client import *
from time import sleep
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
class Signal:
enabled = False
events = []
def button_callback(channel):
Signal.events.append(channel)
class ButtonPress(Client):
button_list = {}
def __init__(self, type, button_list):
Client.__init__(self, type)
for key, value in button_list.iteritems():
self.button_list[key] = value
GPIO.setup(key, GPIO.IN)
GPIO.add_event_detect(key, GPIO.FALLING, callback=button_callback, bouncetime=300)
def resolve_msg(self, msg):
Client.resolve_msg(self, msg)
def handle_event(self, channel):
self.send_status_update(self.button_list[channel])
def send_status_update(self, name):
if len(self.network) != 0:
s = self.construct_update(self.network, name, "pressed")
self.send(s)
def _resolve_update_msg(self, name, payload):
debug_print("resolve update msg: ", name, payload)
def close(self):
Client.close(self)
GPIO.cleanup()
port = 12345
host = socket.gethostname()
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM)
button_list = {15: 'front_door_btn',14: 'balcony_btn'}
ctrl = ButtonPress('button_ctrl', button_list)
ctrl.init_connections(port, host)
count = 0
while(not ctrl.closed):
sleep(0.2)
ctrl.poll_msg([ctrl.server],[],[])
ctrl.update_network()
while (len(Signal.events) != 0):
ctrl.handle_event(Signal.events.pop())server.py
contains all the helper functions for the web server to connect to the local socket
import socket
from client import *
from time import sleep, time
class Signal:
serv = None
class Server(Client):
def resolve_msg(self, msg):
Client.resolve_msg(self, msg)
def set_led(self, name, x):
s = self.construct_update(self.network, name, str(x))
self.send(s)
def init_server():
port = 12345
host = socket.gethostname()
Signal.serv = Server('server')
Signal.serv.init_connections(port, host)
print Signal.serv
while (not Signal.serv.initiated):
Signal.serv.poll_msg([Signal.serv.server],[],[])
Signal.serv.update_network()
print "initiation successful"
def toggleLED(name, status):
Signal.serv.poll_msg([Signal.serv.server],[],[])
Signal.serv.update_network()
Signal.serv.set_led(name, status)
def getLED():
Signal.serv.poll_msg([Signal.serv.server],[],[])
Signal.serv.update_network()
return Signal.serv.get_update('led')
def update_param(name, value):
Signal.serv.poll_msg([Signal.serv.server],[],[])
Signal.serv.update_network()
s = Signal.serv.construct_update(Signal.serv.network, name, str(value))
Signal.serv.send(s)
def poll_until_update_name(name, timeout):
name = name + "_status"
start = time()
time_now = start
# if name not updated before
if not name in Signal.serv.update_msg_list.keys():
while (not name in Signal.serv.update_msg_list.keys()) :
# poll message
Signal.serv.poll_msg([Signal.serv.server],[],[])
Signal.serv.update_network()
# name added to list
if name in Signal.serv.update_msg_list.keys():
return Signal.serv.get_update(name)
# check time out
time_now = time()
if (time_now - start)*1000 > timeout:
print 'time out: ', (time_now - start)*1000
return None
# if name has been updated before, check update version before poll
v = Signal.serv.update_msg_list[name].version
# if version changes, will not enter loop
while (Signal.serv.update_msg_list[name].version == v):
# poll message
Signal.serv.poll_msg([Signal.serv.server],[],[])
Signal.serv.update_network()
# check time out
time_now = time()
if (time_now - start)*1000 > timeout:
print 'time out: ', (time_now - start)*1000
return None
return Signal.serv.get_update(name)
def poll_until_update_names(names, timeout):
start = time()
time_now = start
v_list = {}
# generate a list to keep track of the versioning of the wanted updates
for i in names:
i = i + "_status"
if not i in Signal.serv.update_msg_list.keys():
# if not updated before
v_list[i] = None
else:
v_list[i] = Signal.serv.update_msg_list[i].version
# then we start polling until all the versioning has been updated
# when all the entries is different from the current version list, exit loop
cond = False
while (not cond):
# poll
Signal.serv.poll_msg([Signal.serv.server],[],[])
Signal.serv.update_network()
# check timeout
time_now = time()
if (time_now - start)*1000 > timeout:
print 'time out: ', (time_now - start)*1000
return False
exit_cond = True
for i in names:
i = i + "_status"
if not i in Signal.serv.update_msg_list.keys():
exit_cond = False
break
if v_list[i] == Signal.serv.update_msg_list[i].version:
exit_cond = False
cond = exit_cond
return True
run.py
Flask web server
#! /usr/bin/env python
import sys, os, inspect
currentdir = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(inspect.getfile(inspect.currentframe())))
parentdir = os.path.dirname(currentdir)
sys.path.insert(0,parentdir)
from server import *
import json
from flask import Flask, render_template, redirect, url_for, Response, request, jsonify, send_file
from flask_cors import CORS, cross_origin
from time import sleep,time
from werkzeug.contrib.fixers import ProxyFix
import io
import picamera
import subprocess
app = Flask(__name__)
CORS(app)
class sig:
camera = None
still_stream = None
def shutdown_server():
func = request.environ.get('werkzeug.server.shutdown')
if not func is None:
func()
Signal.serv.close_request()
sleep(0.5)
Signal.serv.close()
@app.route('/')
def homepage():
return render_template('index_bs.html')
@app.route('/video_surveillance')
def video_sur():
sig.detach=False
return render_template('video_surveillance_bs.html')
@app.route('/control')
def control():
return render_template('control.html')
@app.route('/_update', methods = ['GET', 'POST'])
def list_update():
# on control page, update retrieves all the info for the sensors
if 'type' in request.form.keys() and request.form['type'].encode('ascii', 'ignore') == "load":
ids = request.form['attributes'].split(',')
res = {}
for i in range(len(ids)):
ids[i] = ids[i].encode('ascii', 'ignore')
update_param("get_"+ids[i], '0')
poll_until_update_name(ids[i], 1024)
res[ids[i]] = Signal.serv.get_update(ids[i]+'_status')
print res
return json.dumps(res)
# send all the logs
res = []
f = open("activity.log", "r")
f.seek(0)
for line in f:
arr = line.split("$")
if len(arr) == 3:
res = [{"time": arr[0],"event": arr[1],"detail": arr[2][:-1]}] + res
#print res
f.close()
return json.dumps(res)
@app.route('/_control', methods = ['GET', 'POST'])
def param_control():
t = request.form['type'].encode('ascii','ignore')
val = request.form['value'].encode('ascii','ignore')
update_param(t, val)
poll_until_update_name(t, 99999)
sleep(0.4)
print t, Signal.serv.get_update(t+"_status")
return jsonify(status=Signal.serv.get_update(t+"_status"))
@app.route('/_camera_ctrl', methods=['GET','POST'])
def camera_ctrl():
t="snapshot"
#update_param(t, "0")
#poll_until_update_name(t, 99999)
subprocess.Popen("wget http://localhost:8080/?action=snapshot -O ~/final/Server/capture.jpg", shell=True)
sleep(0.5)
filename = "capture.jpg"
return send_file(filename, mimetype="image/jpeg")
@app.route('/shutdown', methods=['POST','GET'])
def shutdown():
shutdown_server()
return 'Server shutting down...'
app.wsgi_app = ProxyFix(app.wsgi_app)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# initialize message host
init_server()
# start camera
#sig.camera = picamera.PiCamera()
#sig.camera.resolution = (320,240)
#sig.still_stream = io.BytesIO()
# run the server
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', debug=False, threaded=True)
client.py
Defines the messaging data structure
import socket
verbose = False
import select
import errno
import sys
def debug_print(*args):
if verbose:
print 'DEBUG_PRINT: ',
for arg in args:
print arg,
print
class Update:
payload = ''
dest = []
version = 0
src = ''
class Message:
update_msg_list = {}
messenger_type = ''
network = []
def construct_update(self, dest, name, payload):
assert type(dest) == list and type(name) == str and type(payload) == str
#if not in list, construct one
if not name in self.update_msg_list.keys():
self.update_msg_list[name] = Update()
update = self.update_msg_list[name]
if len(dest) == 0:
return ''
#set update info
update.payload = payload
update.dest = dest
update.version +=1
update.src = self.messenger_type
dstr = ''
for d in dest:
dstr += ';'+d
return 'U/{}/{}/{}/{}/{}'.format(self.messenger_type,dstr,name,update.version,payload)
def reconstruct_update(self, name):
assert name in self.update_msg_list.keys()
update = self.update_msg_list[name]
#set update info
dstr = ''
for d in update.dest:
dstr += ';'+d
print update.src
msg = 'U/{}/{}/{}/{}/{}'.format(update.src,dstr,name,update.version,update.payload)
print msg
return msg
def update_msg(self, msg):
msg_split = msg.strip("\n").split('/')
#debug_print(msg_split)
i = 0
while(msg_split[i] == ''):
i += 1
src = msg_split[i]
dest = msg_split[i+1].split(';')
if '' in dest:
dest.remove('')
#disgard msg if the message is not for you
if self.messenger_type != 'msg_server' and not self.messenger_type in dest:
return None
#get update name, if not in list, construct one
name = msg_split[i+2]
if not name in self.update_msg_list.keys():
self.update_msg_list[name] = Update()
update = self.update_msg_list[name]
#get version, payload
version = (int)(msg_split[i+3])
payload = msg_split[i+4]
#disgard msg if it is not a newer one
if version <= update.version:
return None
#set update info
update.dest = dest
update.payload = payload
update.version = version
return name
def _resolve_msg(self, s, msg):
pass
def recv(self, s):
buf = ''
while(True):
try:
data = s.recv(1024)
except socket.error, e:
err = e.args[0]
if err == errno.EAGAIN or err == errno.EWOULDBLOCK:
debug_print ('message recv: No data available')
break
else:
# Something else happened, handle error, exit, etc.
print e
sys.exit(1)
else:
if data:
#debug_print('received message', data)
buf += data
else:
print "message recv fails"
self.handle_lose_connection(s)
break
line_list = buf.split('\n')
for line in line_list:
self._resolve_msg(s, line)
def update_print(self, s):
if s in self.update_msg_list.keys():
x = self.update_msg_list[s].payload
print x
def get_update(self, s):
if s in self.update_msg_list.keys():
x = self.update_msg_list[s].payload
return x
else:
return None
def handle_lose_connection(self, s):
print "lose_connection"
if not s is None:
s.close()
class Client(Message):
connected = False
initiated = False
messenger_type = ''
server = None
network = []
closed = False
def __init__(self, messenger_type):
self.messenger_type = messenger_type
def try_connect(self, port, host):
try:
self.server.connect((host, port))
debug_print("client try connect: connected!")
except:
print "message server not found!"
self.close()
def init_connections(self, port, host):
sock = socket.socket()
self.server = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
self.try_connect(port, host)
self.connected = True
self.server.setblocking(0)
def send(self, msg):
try:
self.server.send(msg+'\n')
except:
print "not able to send"
self.handle_lose_connection(self.server)
def poll_msg(self, reads, writes, excepts):
assert type(reads) == list and type(writes) == list and type(excepts) == list
readable, writable, exceptional = select.select(reads, writes, excepts, 0)
for s in readable:
self.recv(self.server)
def update_network(self):
if 'network' in self.update_msg_list.keys():
self.network = self.update_msg_list['network'].payload.split(';')
# =========== helper function =============================
def close(self):
print "closing"
self.server.close()
self.closed = True
def _resolve_update_msg(self, name, payload):
pass
def close_request(self):
print "sending close request"
self.send('X:'+self.messenger_type)
#self.close()
def _resolve_msg(self, s, msg):
if msg == '':
return
Message._resolve_msg(self, self.server, msg)
if msg[0] == 'T':
self.send('T/' + self.messenger_type + '/')
debug_print('client resolve msg: ', "sending type to host")
if msg[0] == 'I':
self.initiated = True
self.send('I/' + self.messenger_type + '/')
debug_print('client resolve msg: ', 'system initiated!')
if msg[0] == 'C':
debug_print(msg)
if msg[0] == 'U':
debug_print ('client resolve msg: ', 'update', msg)
name = self.update_msg(msg[1:])
debug_print(name)
if name in self.update_msg_list.keys():
debug_print ('client resolve msg: ', self.update_msg_list[name].payload)
self._resolve_update_msg(name, self.update_msg_list[name].payload)
if msg[0] == 'X': #shutdown system
print "receive shut down"
debug_print ('closing socket... shutting down system', self.messenger_type)
self.close()
def handle_lose_connection(self, s):
self.close()
#Message.handle_lose_connection(self, s)
#if not self.closed:
#self.connected = False
#self.initiated = False
#self.network = []
#self.port = 12345
#self.host = socket.gethostname()
#self.init_connections(self.port, self.host)
security_center.py
controls the entire security system
import socket
from client import *
from time import sleep,ctime,time
import subprocess
class Signal():
connected = False
initiated = False
time = 0
'''A security center does the following:
1. actively logs the events into a local file
2. logging level is based on security mode
3. takes picture
4. scans the apartment based on security mode
5. responds to clicks based on security mode'''
class SecurityCenter(Client):
mode = 0 # 0: manual, 1: easy secure, 2: front door focused, 3: heavily logged
filename = ""
def __init__(self, type, mode = 1, filename = "activity.log"):
Client.__init__(self, type)
self.mode = mode
self.filename = filename
def resolve_msg(self, msg):
if msg == '':
return
if self.mode == 3:
if msg[0] == 'I':
self.log_msg("Initialized", self.messenger_type)
if msg[0] == 'X':
self.log_msg("Closing", self.messenger_type)
Client.resolve_msg(self, msg)
def log_msg(self, event, detail):
cmd = "echo '" + ctime(time()) + '$' + event + '$' + detail + "' >> " + self.filename
print cmd
subprocess.Popen(cmd, shell=True)
def clr_log(self):
subprocess.Popen("echo '' > " + self.filename, shell=True)
def send_status_update(self, name, payload):
if len(self.network) != 0:
s = self.construct_update(self.network, name+'_status', str(payload))
self.send(s)
def _resolve_update_msg(self, name, payload):
debug_print("resolve update msg: ", name, payload)
if name == "set_mode":
self.mode = int(payload)
Signal.time = time()
self.log_msg("set_mode", payload)
self.send_status_update(name, payload)
return
if self.mode == 2:
if name == "front_door_btn":
self.send(self.construct_update(self.network, "servo_setmode", "0"))
if name == "balcony_btn":
self.send(self.construct_update(self.network, "servo_setmode", "1"))
return
if name == "get_mode":
self.send_status_update(name, str(self.mode))
if name == "clr_log":
self.clr_log()
self.send_status_update(name, payload)
return
if self.mode == 1 or self.mode == 3:
# move when triggered
if name == "front_door_btn":
s = self.construct_update(self.network, "target_front_door", "0")
self.send(s)
self.log_msg(name, payload)
self.log_msg("target_front_door", "action detected")
elif name == "balcony_btn":
s = self.construct_update(self.network, "target_balcony", "0")
self.send(s)
self.log_msg(name, payload)
self.log_msg("target_balcony", "action detected")
else:
if self.mode == 3:
self.log_msg(name, payload)
def close(self):
Client.close(self)
port = 12345
host = socket.gethostname()
demo_events = {
3.00: {"bedroom_light_1":"true", "bedroom_light_2": "true"},
6.00: {"dining_room_light_1":"true"},
9.00: {"dining_room_light_1" : "true"},
12.00: {"living_room_light_1":"true"},
15.00: {"living_room_light_1" : "false", "bedroom_light_1":"false", "bedroom_light_2": "false"}
}
demo_events_time = demo_events.keys()
demo_events_time.sort()
ctrl = SecurityCenter('security_center', 1, "activity.log")
ctrl.init_connections(port, host)
Signal.time = time()
Signal.ind = 0
count = 0
while(not ctrl.closed):
sleep(0.1)
ctrl.poll_msg([ctrl.server],[],[])
ctrl.update_network()
if ctrl.mode == 2:
if time()-Signal.time >= demo_events_time[Signal.ind]:
Signal.ind += 1
if Signal.ind >= len(demo_events_time):
Signal.ind = 0
for key in demo_events[demo_events_time[Signal.ind]]:
s = ctrl.construct_update(ctrl.network, key, demo_events[demo_events_time[Signal.ind]][key])
ctrl.poll_msg([ctrl.server],[],[])
print s
ctrl.send(s)
if Signal.ind == 0:
Signal.time = time()
server.sh
an elegant starting script for the system
#! /bin/bash
if pgrep pigpiod
then
echo 'got daemon running'
else
pigpiod
fi
if pgrep mjpg_streamer > /dev/null
then
echo 'mjpg_streamer already running'
else
LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/home/pi/mjpg-streamer/mjpg-streamer-experimental
mjpg_streamer -o 'output_http.so -w ./www' -i 'input_raspicam.so -fps 25 -x 640 -y 480 -q 65 -hf -sh 25 -vs' &
fi
python ../message.py &
sleep 1
python ../led_controller.py &
python ../servo_controller.py &
python ../buttons.py &
python ../security_center.py &
python run.py
if pgrep mjpg_streamer
then
kill $(pgrep mjpg_streamer) > /dev/null 2>&1
echo 'mjpg_streamer stopped'
else
echo 'mjpg_streamer not running'
fi
if pgrep python
then
killall python
echo 'python process killed'
fi